🙂 이번 시간에는 객체(참조값)의 얕은 복사, 깊은 복사을 알아보고, 깊은 복사를 하는
StructuredClone도 알아보았다.
1. 값을 복사하는 법
JS에서 원시값, 참조값의 개념과 복사 방식의 차이 를 대해 알고 있다면 “2. 객체의 얕은 복사, 깊은 복사”로 바로 넘어가자
1) 원시값을 복사하는 경우
- JS에서는 원시값(Number, String, Boolean, Null, Undefined), 참조값(Object, Array)이 존재한다.
- 원시값을 저장한 변수는 실제 데이터값이 저장되는데, 변수(
cloneValue)의 값을 변경해도originalValue의 값이 변경되지 않는다.
let originalValue = 12;
let cloneValue = originalValue; // 12
cloneValue = 22;console.log(originalValue); // 12
console.log(cloneValue); // 222) 참조값을 복사하는 경우
- 원시값과 달리 참조값(객체, 배열 등)을 변수에 저장할 때는 독립적인 메모리 공간에 실제값을 저장하고,
- 변수에는 실제값이 아닌, 실제값을 담고 있는 메모리 위치(주소)값을 저장한다!
- 이 때문에 참조값을 원시값처럼 복사하면, 메모리 주소값을 복사하기에 값을 변경하면 같이 변경된다.
const originalValue = { name: 'haha', age: 12 };
const cloneValue = originalValue; // { name: 'haha', age: 12 }
cloneValue.name = 'lala';// cloneValue의 값을 변경했지만, originalValue의 값도 영향을 받음
console.log(originalValue); // { name: 'lala', age: 12 }
console.log(cloneValue); // { name: 'lala', age: 12 }- 그렇다면 참조값(Object, Array 등)은 어떤 방식으로 복사하여 값만을 복사할 수 있을까?
- 객체의 얕은 복사, 깊은 복사와 함께 알아보자!
2. 객체의 얕은 복사, 깊은 복사
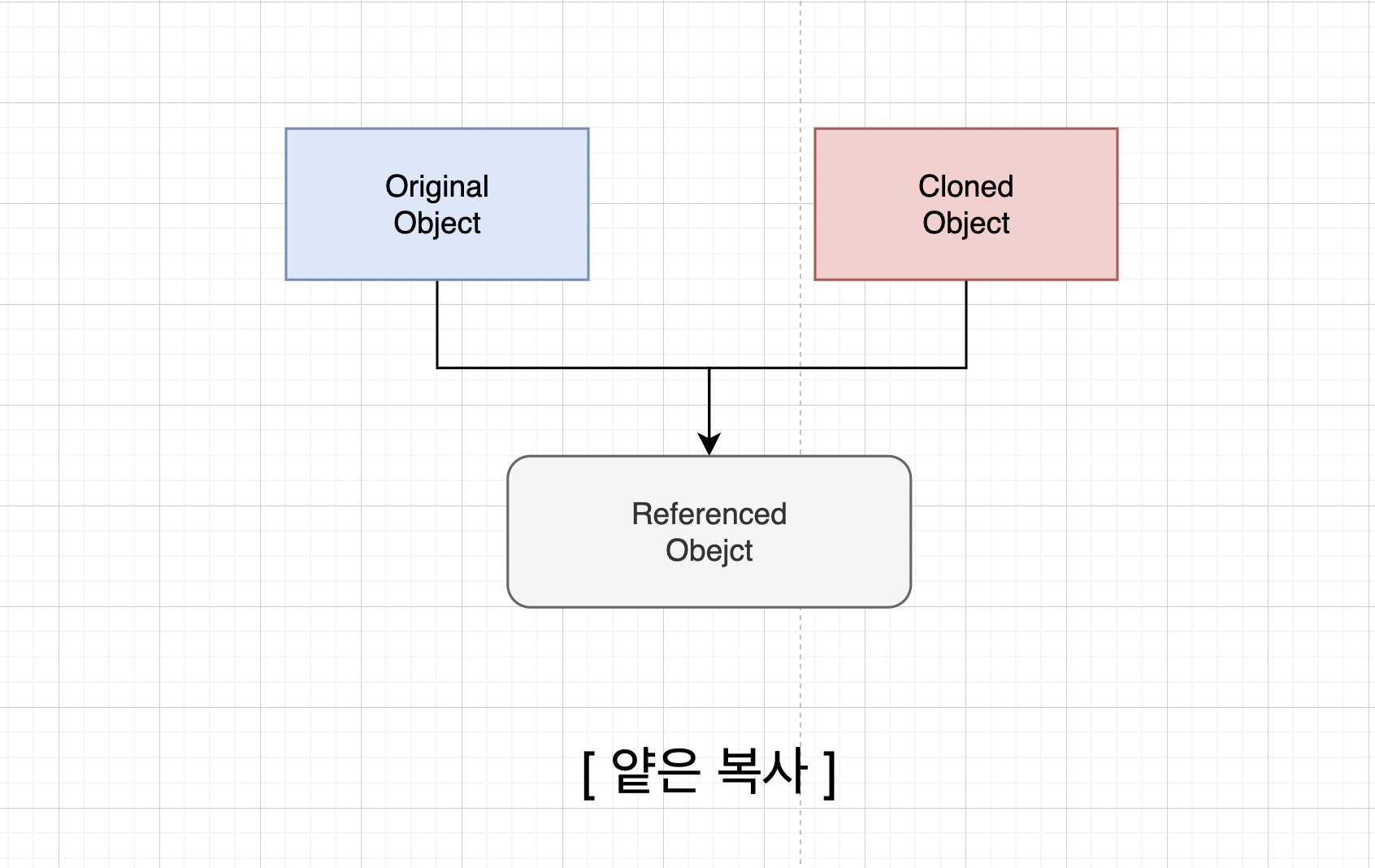
📌 얕은 복사는 참조값을 복사하고, 깊은 복사는 객체의 실제 값을 복사한다.
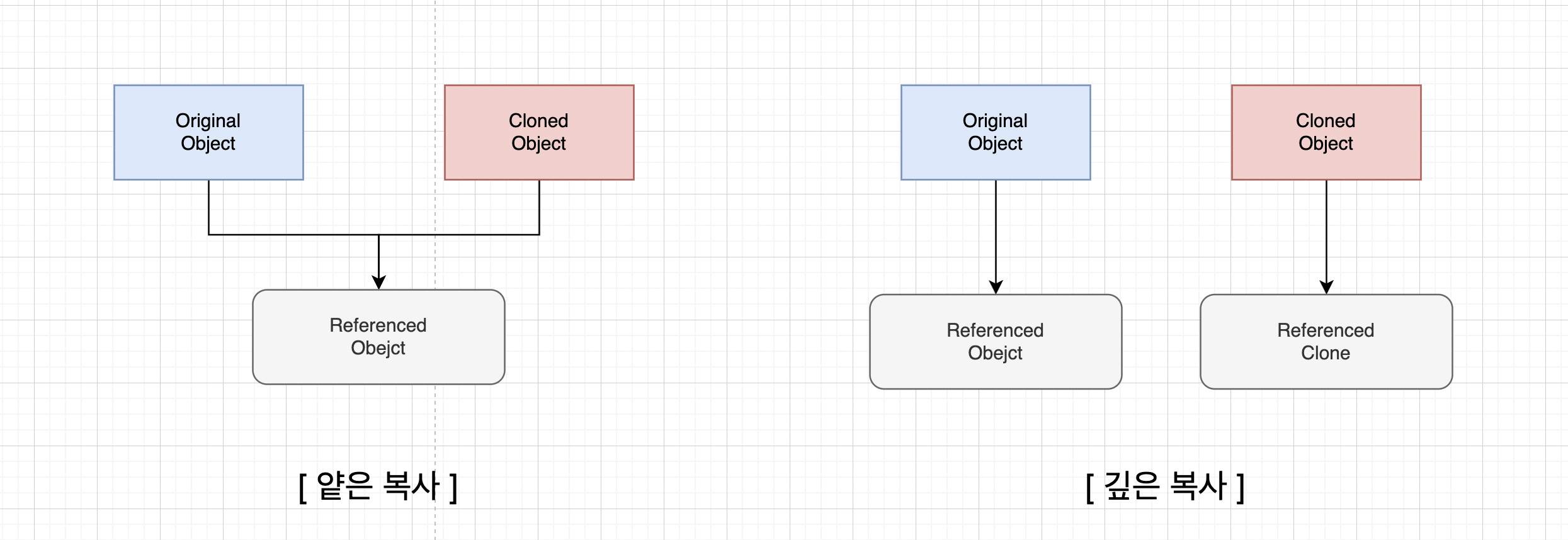
- 객체를 복사하는 방법에는
Object.assign,Spread Operator,JSON.parse,StructuredClone등이 있는데, 각각의 예시와 함께 복사 유형(얕은, 깊은 복사)을 살펴보자.
1) Object.assign
(1) Object.assign이란?
Object.assign는target에source를 병합한 값을 리턴해주는데,target값도 함께 변한다.
const returnValue = Object.assign(target, source);const target = { name: 'haha', age: 21 };
const source = { age: 3, etc: '...' };
const returnedTarget = Object.assign(target, source);
console.log(target) // {name: "haha", age: 3, etc: "..."}
console.log(returnedTarget); // {name: "haha", age: 3, etc: "..."}(2) 얕은 복사를 하는 Object.assign
Object.assign(target, source)로 객체를 복사할 때는target을 빈 객체({})로 두고 복사하고 싶은 객체를source에 넣어주면 된다.- 아래 예시를 보면 알 수 있듯이
cloneObj의 값을 변경해도original의 값은 영향을 받지 않는다.
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12 };
const cloneObj = Object.assign({}, original); // 복사하기
cloneObj.age = 22;
console.log(original); // {name: "haha", age: 12}
console.log(cloneObj); // {name: "haha", age: 22}- 단, 복사할 객체에 객체(
option)가 있고, 이 객체(option)의 값을 변경하면 같이 변경된다(얕은복사)
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } };
const cloneObj = Object.assign({}, original);
cloneObj.option.address = 'NewYork';
console.log(original); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }
console.log(cloneObj); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }- 만약
cloneObj의option값만 변경하고 싶다면 객체 자체를 재할당하면 된다.
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } };
const cloneObj = Object.assign({}, original);
cloneObj.option = { address: 'NewYork' }; // this!
console.log(original); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } }
console.log(cloneObj); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }2) Spread Operator
(1) Spread Operator이란?
- Spread Operator(…)는 반복가능한 객체에서 사용할 수 있는 연산자이다.
- 배열의 병합, 복사, 객체의 복사 등에 사용된다.
const arr1 = [1,2,3,4];
const arr2 = [5,6,7,8];
console.log([...arr1, ...arr2]); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8](2) 얕은 복사를 하는 Spread Operator
Spread Operator로 객체를 복사할 시, 복사한 객체의 값을 변경해도 원본에는 영향을 주지 않는다.
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12 };
const cloneObj = {...original}; // 복사하기
cloneObj.age = 22;
console.log(original); // {name: "haha", age: 12}
console.log(cloneObj); // {name: "haha", age: 22}- 단,
Spread Operator도 복사할 객체 내부에 객체가 있고, 이 객체의 값을 변경할 시Object.assign처럼 얕은 복사로 작동된다.
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } };
const cloneObj = {...original};
cloneObj.option.address = 'NewYork';
console.log(original); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }
console.log(cloneObj); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }3) JSON.parse & JSON.stringify
(1) JSON.parse & JSON.stringify이란?
JSON.parse는 String객체를 Json 객체로,JSON.stringify는 Json객체를 String객체로 변환한다.
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };
const strObj = JSON.stringify(obj);
const parsedObj = JSON.parse(strObj);
console.log(strObj); // '{"a":1,"b":2}'
console.log(parsedObj); // {a: 1, b: 2}(2) 깊은 복사를 하는 JSON.parse & JSON.stringify
- 복사할 객체를
String객체로 변경하고String객체를Json객체로 변경하면 깊은 복사가 가능하다. - 단, 이 방법은 성능이 그다지 좋지 않다는 단점이 있다.
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } };
const cloneObj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(original)); // 복사하기
cloneObj.option.address = 'NewYork';
console.log(original); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } }
console.log(cloneObj); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }4) StructuredClone
(1) StructuredClone이란?
StructuredClone은 주어진 value에 대해 깊은 복사를 한다.- 앞서 살펴 본,
JSON.parse&JSON.stringify보다 성능이 좋다.
structuredClone(value);(2) 깊은 복사를 하는 StructuredClone
- 사용법은 아래와 같이 간단하며, 참조값이 아닌 객체의 값 자체를 복사한다.(깊은 복사)
const original = { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } };
const cloneObj = structuredClone(original); // 복사하기
cloneObj.option.address = 'NewYork';
console.log(original); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'Seoul' } }
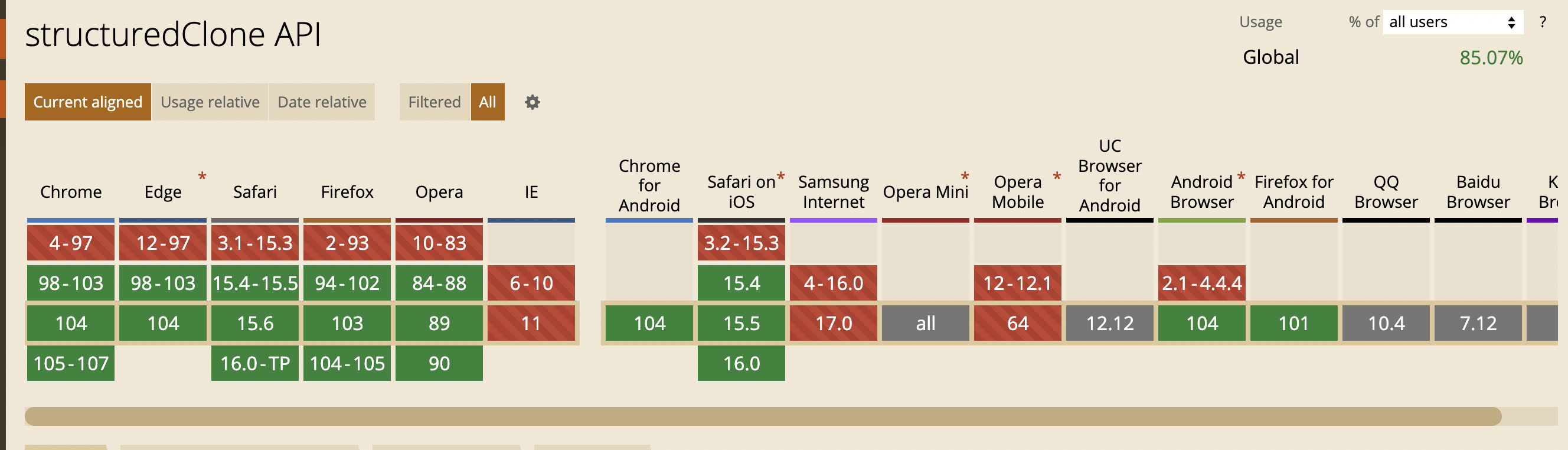
console.log(cloneObj); // { name: 'haha', age: 12, option: { address: 'NewYork' } }- (포스팅 시점) 사용가능한 브라우저는 아래와 같다. (호환가능한 브라우저 보기)
반응형
'개발 기술 > 사소하지만 놓치기 쉬운 개발 지식' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JS/Eslint] 레이스컨디션을 유발하는 await는 쓰지말자(require-atomic-updates) (0) | 2022.09.03 |
|---|---|
| [JS/Eslint] 반복문에서 await를 쓰지말자(no-await-in-loop) (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| [SASS/SCSS] hex, rgb 컬러에 투명도 주는 방법 (0) | 2022.07.23 |
| [CSS/JS] vh 버그 해결방법(dvh 사용법, js 계산법) (0) | 2022.07.17 |
| [CSS] Container 쿼리(특정 요소 크기에 따라 스타일링하기) (0) | 2022.07.03 |





댓글